How to manage economic risk in international business
By expanding your business internationally, you can reach new customers, make more money, and grow your business. But it also puts your business at risk of economic problems that don’t happen when you do business in your own country. Knowing how to deal with these risks can make the difference between doing well in business abroad and losing a lot of money.
When businesses do business internationally, they face economic risk, which is the chance that they will lose money because of sudden changes in the economy in other countries. These changes can have effects on a wide range of things, from currency exchange rates to how much money consumers have to spend. These effects may not be immediately clear, but they can have a big impact on your bottom line.
The fact that the world economy is connected means that things that happen in one country can have effects all over the world. Changes in government policies, currency devaluation in emerging markets, or inflation spikes in developed economies can all have an effect on your international operations. Companies that don’t deal with these risks often lose money they didn’t expect to lose, have lower profits, or even have to leave some markets completely.
This complete guide will look at the different kinds of economic risks you will face in international business and give you useful tips on how to deal with them. You’ll learn from real-life examples and find useful tools that can help your business stay safe while taking advantage of international opportunities.
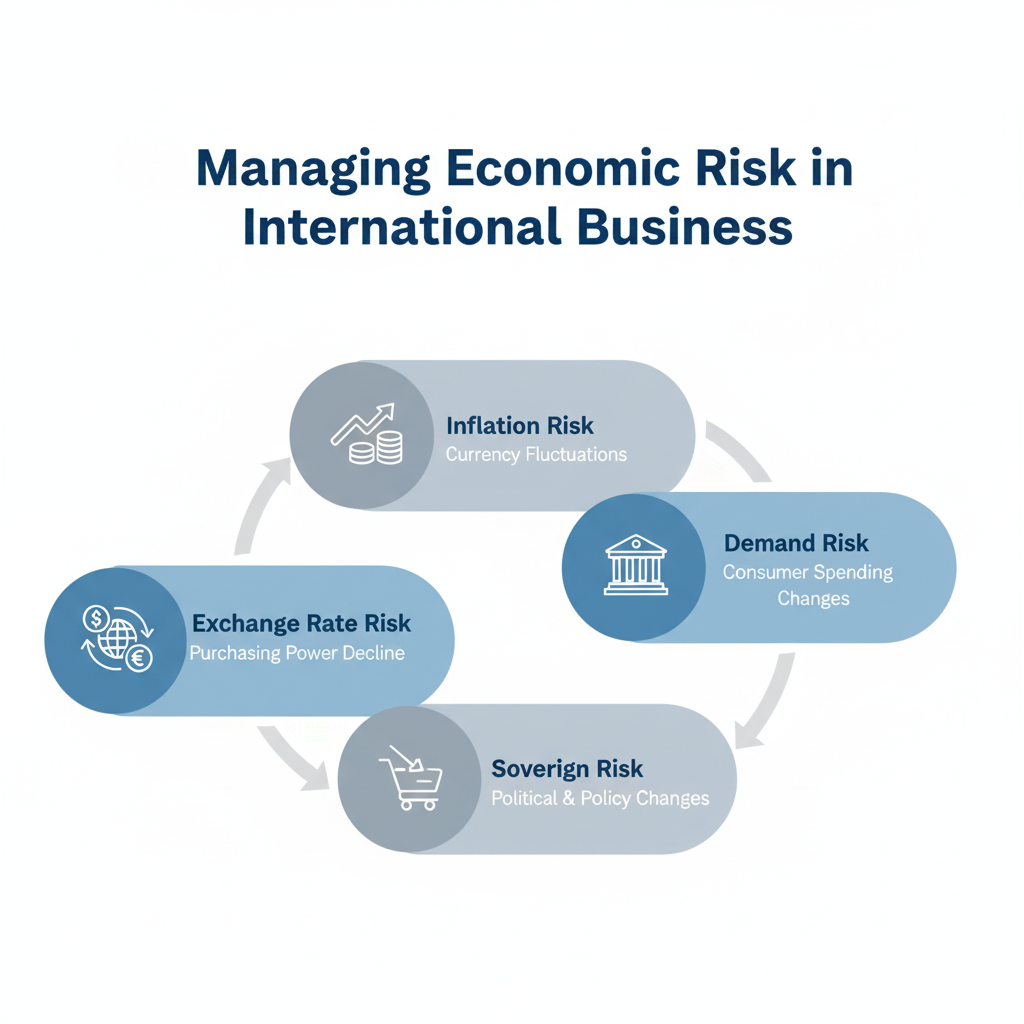
Learning about the Four Main Types of Economic Risk
Exchange Rate Risk: When Currencies Change Value
Currency risk, or exchange rate risk, happens when changes in currency values have an effect on your business deals. This is one of the most common types of economic risk in international business, and it affects businesses of all sizes.
How the risk of changes in the exchange rate affects your business:
- Changes in revenue when you change foreign sales back to your home currency
- Increased costs for imported materials or services
- When your currency gets stronger against your competitors’ currencies, you have a competitive disadvantage.
- Balance sheet impacts on foreign subsidiaries and investments
Effect in the Real World:
Think about a U.S. business that sells things in Europe. If the Euro falls by 10% against the Dollar, the company’s European revenue drops by 10% when it is converted back to Dollars, even if sales stay the same.
Inflation Risk: The Cost Multiplier That Isn’t Obvious
Inflation risk in international business means that different countries have different inflation rates, which can lower your buying power and profit margins. This economic risk factor is especially hard to deal with because inflation hits different countries at different times and rates.
Key Inflation Risk Challenges:
- The cost of materials and labor in the area is going up.
- People in markets with high inflation have less money to spend.
- Difficulty in accurate long-term pricing and budgeting
- Costs of the supply chain go up differently in each country.
Things to think about strategically:
Businesses that work in markets with high inflation rates have to constantly change how they set prices and how much things cost. If inflation rises faster than expected, a contract that looks good right now could end up costing you money in a few months.
Sovereign Risk: When Countries Change the Rules
Sovereign risk, also known as country risk, is the chance that a government will change rules that affect how your business runs. Changes in tax laws, trade rules, monetary policies, or even political instability that affect the economy are all examples of this.
Different kinds of sovereign risk:
- Changes to tax rates or structures
- New tariffs or trade barriers
- Currency controls that make it hard to send money
- Taking over foreign assets by the government
- Economic sanctions that hurt trade ties
Why Sovereign Risk Matters:
Sovereign risk is different from other economic risks because it is caused by governments making deliberate policy choices. These changes can happen quickly and may only affect foreign companies or certain industries.
Demand Risk: When changes in the economy affect how people act
Demand risk occurs when economic conditions in a country affect consumer purchasing patterns, business investment levels, or overall market demand for your products or services. This kind of economic risk is very closely related to the overall health of the economies in your target markets.
Things That Affect Demand Risk:
- Economic recessions reducing consumer spending
- Changes in income levels that change how much people can buy
- Changes in business investment because of uncertainty in the economy
- Unemployment rates affecting demand in the market
- Long-term market potential is affected by patterns of economic growth.
Ways to Handle Economic Risk That Have Worked Before
Hedging: Your Insurance Policy for Your Money
Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset potential losses from economic risk exposure. This strategy is particularly effective for managing exchange rate risk and some aspects of inflation risk.
Common hedging tools::
- Forward contracts that set exchange rates for future trades
- Currency options that protect you while still giving you the chance to make money
- Currency swaps for businesses that work in more than one country
- Commodity futures to deal with changes in input costs
Putting Effective Hedging into Action:
A full risk assessment will help you figure out what risks you are most exposed to. Find out which risks could hurt your business the most and then hedge against those risks first. A lot of businesses hedge 50–80% of their short-term foreign exchange exposure, but they leave some positions unhedged so they can take advantage of good moves.
The best ways to hedge are:
- Check your hedging strategy often and change it as needed based on how your business is doing.
- Use more than one hedging tool to make your approach more balanced.
- Think about how much it will cost to hedge against the risk.
- Maintain clear documentation and reporting procedures for all hedging activities
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket; spread them out.
Geographic and operational diversification is one of the most effective long-term strategies for managing economic risk in international business. You don’t have to rely on any one economy as much if you do business in more than one country and market.
Strategies for Geographic Diversification:
- Enter markets at different times in the economic cycle to spread out your risk.
- Set up shop in both developed and developing markets
- Think about diversifying your investments across different regions to lower the correlation between markets.
- Find a balance between markets that are growing quickly and those that are stable and mature.
Operational Diversification:
- Spread out your supply chain across several countries.
- Build up your ability to source goods locally so you don’t have to rely on imports as much.
- Make production capabilities that can easily switch between markets.
- To lower concentration risk, build a diverse customer base.
How to Put It Into Action:
Diversification should happen slowly and with a plan, not quickly into many markets at once. Do a lot of research on the market and run pilot programs before putting a lot of money into new markets.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies: Changing with the Economy
Pricing strategies in international markets need to take into account a number of economic risks, such as inflation, changes in currency value, and changes in demand. With dynamic pricing, you can change prices based on how the economy is doing while still being competitive.
Parts of a pricing strategy:
- Currency adjustment mechanisms that change prices automatically when the exchange rate changes
- Long-term contracts with clauses that let inflation rise
- Local pricing strategies that take into account how much people can afford to buy
- Analysis of competitive pricing that takes into account the state of the local economy
Advanced Pricing Techniques:
- Natural hedging through local cost structures that change with local income
- Transfer pricing strategies that optimize tax efficiency while managing risk
- Value-based pricing that takes into account the state of the local economy
- Dynamic contract terms that spread the risk between buyers and sellers
Protection for your money and insurance
Different types of insurance and financial products can help protect against certain types of economic risk, especially sovereign risk and big changes in currency value.
Different kinds of international business insurance are:
- Insurance against political risk that protects your business from government actions
- Export credit insurance to protect trade finance
- Currency insurance for big changes in exchange rates
- Business interruption insurance that pays for economic problems
Programs Supported by the Government:
A lot of countries have government-backed insurance plans for doing business in other countries. These programs often cost less than private insurance and may cover risks that private insurers won’t.
Real-World Case Studies in Economic Risk Management
A tech company that deals with currency risk
A software company that did a lot of business in Europe was at a lot of risk because the Euro’s value changed compared to their home currency. They used a full hedging strategy that included:
- Forward contracts that cover 70% of the expected Euro income for the next year
- Currency options to protect against big changes
- Setting up European development centers to create Euro-denominated costs is a natural way to hedge.
Results: The company cut earnings volatility by 60% but kept the chance of making more money from good currency movements.
Manufacturing Firm Addressing Inflation Risk
A manufacturing company that does business in a number of Latin American countries where inflation is high came up with a plan that had many parts:
- IPut in place automatic price adjustment systems that are linked to local inflation rates
- Made deals for supplies that included clauses that let prices go up with inflation
- Set up relationships with local suppliers to make natural hedges
- Used bonds that were linked to inflation to match the structures of assets and liabilities
Outcome: Even though inflation rates were over 20% in some markets, the company kept its profit margins stable and kept doing business in all of its target countries.
Managing Sovereign Risk in a Retail Chain
An international retail chain faced increasing sovereign risk in several emerging markets due to changing regulations and tax policies. They used the following methods to manage risk:
- By operating in more than 15 countries, they reduce their risk of being exposed to just one country.
- Maintaining flexible lease agreements that allowed for quick market exits
- Working with local partners to make it easier to deal with changes in the law
- Buying political risk insurance for big investments
Effect: When regulatory changes made it impossible for competitors to stay in some markets, the company’s diversified approach let them keep growing overall while changing how they did business in those areas.
Making Your Economic Risk Management Framework
Checking and Evaluating Risks
Comprehensive risk assessment and ongoing monitoring systems are the first steps in good economic risk management. This means finding, measuring, and keeping track of the different economic risks that your international operations face.
Key Assessment Components:
- Quantitative examination of currency exposure throughout all business divisions.
- Stress testing to understand potential impacts of economic scenarios
- Regular monitoring of economic indicators in target markets
- Including risk metrics in regular business reports
Systems for Monitoring:
- Daily tracking of currency exposures and market movements
- Monthly reports on economic risk to top management
- Quarterly strategic reviews of risk management policies
- Updates to the full risk assessment every year
Making rules for managing risk
Make clear, detailed rules that tell your organization how to handle economic risk. These policies should include how decisions are made, how much risk is acceptable, and how to handle different types of risks.
Parts of the Policy:
- A clear definition of the levels of risk tolerance for different kinds of economic risk
- Approval processes for decisions about hedging transactions and managing risk
- Rules for reporting and talking to each other
- Policies and procedures should be reviewed and updated on a regular basis.
Technology and Tools for Risk Management
Modern technology gives international businesses advanced tools for keeping an eye on and controlling economic risk. These tools can automate a lot of risk management tasks and give you information about risk exposures in real time.
Technology Solutions:
- Treasury management systems that keep track of currency risks and hedge positions
- Platforms for economic data that give live market information
- Risk analytics software that shows how different economic situations could affect things
- Automated hedging platforms that carry out trades based on rules that have already been set
Advanced methods for managing economic risk
Natural Hedging Strategies
Natural hedging means setting up your business in a way that makes it easier to deal with economic risks. This method can save you money compared to financial hedging and lower your risk over the long term.
Ways to naturally hedge:
- Making sure that the currencies used for revenue and costs are the same in each market
- Establishing production facilities in major sales markets
- Making sure that your assets and debts in foreign currencies are balanced
- Building supply chains that automatically change based on the economy
Scenario Planning and Stress Testing
Planning for different scenarios on a regular basis helps you understand how changes in the economy could affect your business and get ready for them. This forward-thinking way of doing things is important for managing risks ahead of time.
Parts of Scenario Planning:
- Creating a range of economic scenarios, from mild to severe
- Examination of possible effects on income, expenses, and cash flow
- Finding the trigger points that will set off risk management responses
- Regular updates based on how the economy and business operations are changing
Part of the Overall Business Strategy
You shouldn’t treat economic risk management as a separate function; it should be fully integrated with your overall business strategy. This integration makes sure that risk factors affect strategic decisions and that risk management helps the business reach its goals.
Ways to integrate:
- Make sure to include risk assessments in all decisions about expanding internationally.
- Make sure that the goals of risk management are in line with the goals of the whole business.
- Make sure that risk management teams are involved in the planning of strategies.
- When looking at international opportunities, think about returns that take risk into account.
What to Do Next: Your Next Steps in Managing Economic Risk
To manage economic risk in international business, you need to take a systematic, proactive approach that changes as your business and the world around you do. The strategies in this guide will help you protect your international operations while also giving you the best chances for growth.
Not only do you need to find opportunities in international markets, but you also need to know how to handle the risks that come with those opportunities. Companies that are good at managing economic risk often find that their risk management skills give them an edge over their competitors, letting them enter markets and go after opportunities that their competitors avoid because they are worried about risk.







