What is hedging in finance
The stock market can be hard to predict. One day your investments are doing great, and the next day they’re tanking because the market is acting strangely. A lot of investors can’t sleep at night because they’re worried about how to keep their hard-earned money safe from sudden drops in the market.
Hedging offers a solution to this age-old problem. You can think of it as an insurance policy for your investments. It helps you avoid losing money while still letting you take part in market gains. If you know how to hedge, it can mean the difference between sleeping soundly and always worrying about your financial future, whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out.
This complete guide will teach you everything you need to know about hedging in finance, from the basics to more complicated strategies. You’ll discover how hedging works in simple terms, explore various hedging techniques, and learn when and how to implement these strategies in your own investment approach.
Hedging: The Key to Managing Risk
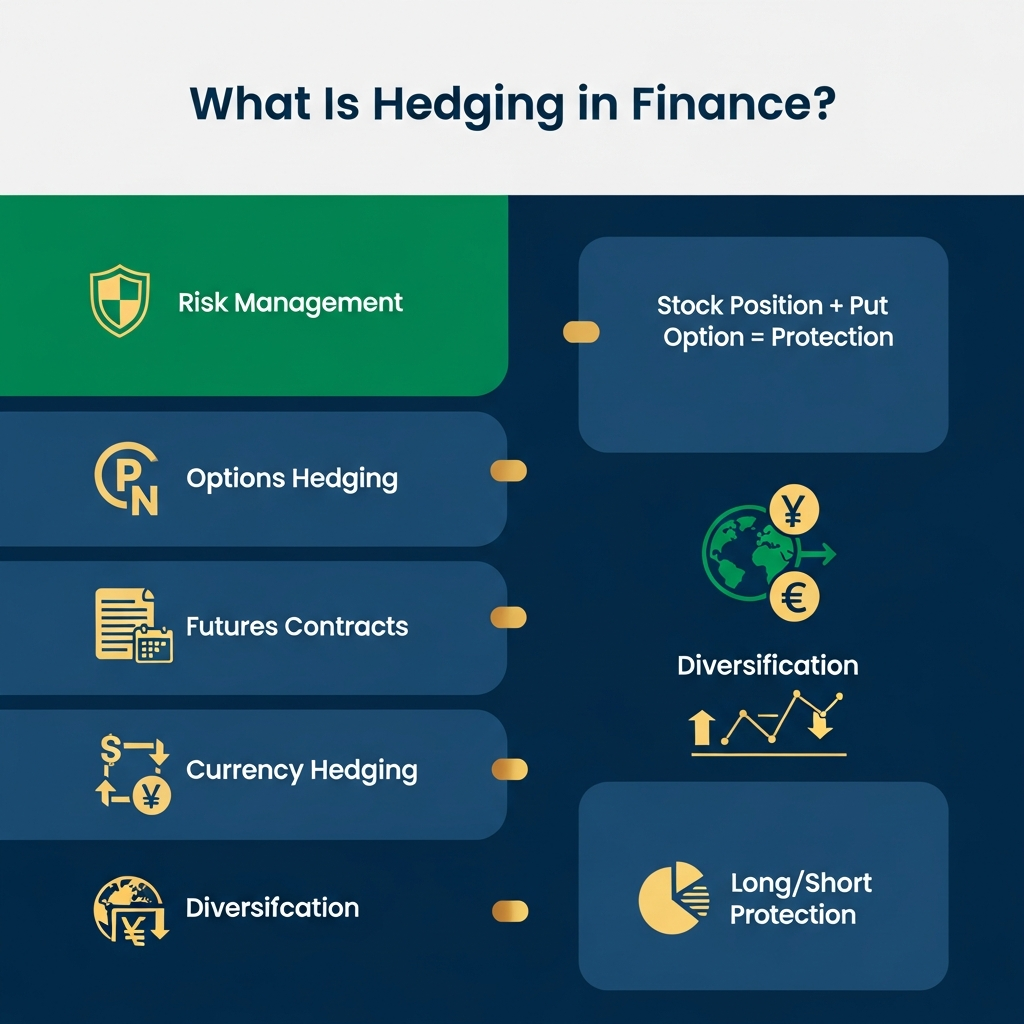
In finance, hedging means taking a position in a related security or financial instrument that cancels out another position in order to lower the risk of price changes that are bad for an asset. It’s a way to manage risk that protects your investments from losing money.
The main goal of hedging in finance is not to make money, but to lose as little money as possible. When you hedge, you’re basically buying insurance against bad changes in the market. Smart investors don’t trade in volatile markets without the right hedging strategies, just like you wouldn’t drive without car insurance.
How Hedging Works in Real Life
Imagine you own 100 shares of a technology stock worth $10,000. You’re worried that the market might be unstable in the next three months. You could buy put options on the same stock to protect yourself from this position. If the stock price falls, the put options increase in value, offsetting some of the losses from your stock position.
This example shows the main idea behind hedging: making two positions negatively correlated so that losses in one position are offset by gains in the other.
Hedging Strategies: Your Tools for Managing Risk
To manage risk well, you need to know about different hedging strategies. Here are the most common ways that both individual and institutional investors go about their business.
1. Derivatives-Based Hedging Futures Contracts
Futures Contracts
Futures contracts allow you to lock in a specific price for an asset at a future date. Farmers commonly use futures to hedge against price fluctuations in their crops. For example, a corn farmer might sell corn futures contracts to guarantee a specific price for their harvest, protecting against potential price drops.
Options Strategies
Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. Put options act as insurance policies for long positions, while call options can hedge short positions. The flexibility of options makes them popular among retail investors.
Swaps
Interest rate swaps and currency swaps are sophisticated instruments primarily used by corporations and financial institutions. These contracts allow parties to exchange cash flows or currencies, providing protection against interest rate or currency fluctuations.
2. Portfolio Hedging
Diversification
The most basic form of hedging involves spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions. This approach reduces concentration risk and helps smooth portfolio volatility over time. me.
Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation involves maintaining a balanced mix of stocks, bonds, and other investments. During market downturns, bonds often perform better than stocks, providing a natural hedge.
3. Currency Hedging
Forward Contracts
International businesses use forward contracts to lock in exchange rates for future transactions. This protects against adverse currency movements that could impact profit margins.
Currency ETFs
Exchange-traded funds focused on specific currencies or currency baskets provide an accessible way for individual investors to hedge currency exposure.
The Three Most Common Hedging Strategies
When discussing what are the 3 common hedging strategies, most financial professionals focus on:
- Long/Short Equity Strategy: Taking long positions in undervalued stocks while shorting overvalued ones
- Options-Based Hedging: Using put and call options to protect existing positions
- Currency Hedging: Protecting against foreign exchange rate fluctuations
These strategies form the backbone of most hedging programs due to their effectiveness and relative accessibility.
Benefits of Hedging: Why Risk Management Matters
Volatility Reduction
Hedging significantly reduces portfolio volatility, creating smoother returns over time. This stability is particularly valuable for investors nearing retirement or those with specific income requirements.
Downside Protection
While hedging can limit upside potential, it provides crucial protection during market downturns. The 2008 financial crisis and the 2020 COVID-19 market crash demonstrated the value of proper hedging strategies.
Improved Sleep Quality
The psychological benefits of hedging shouldn’t be underestimated. Knowing that your investments are safe from big losses can help you make better decisions and lower your stress.
Business Continuity
Hedging helps businesses keep running even when the market is unstable. Airlines hedge fuel costs, importers hedge currency exposure, and manufacturers hedge commodity prices to keep their operations predictable.
Risks and Drawbacks of Hedging
Cost Considerations
There is a cost to hedging. Over time, options premiums, futures margins, and other hedging costs can cut into your returns. These costs must be weighed against the potential benefits of protection.
Opportunity Cost
When the market is going up strongly, hedging could mean you miss out on big gains. The protective put option that saves you during a crash also limits your participation in market recoveries.
Complexity and Timing
To use good hedging strategies, you need to know how and when to do it. Poor execution can result in inadequate protection or unnecessary costs.
Over-Hedging Risks
Excessive hedging can turn a portfolio overly conservative, potentially failing to meet long-term growth objectives.
Speculation vs Hedging: Understanding the Key Differences
Speculation involves taking positions to profit from anticipated price movements, while hedging aims to reduce existing risk exposure. Speculators seek to maximize profits through directional bets, while hedgers prioritize risk reduction over profit maximization.
Some of the most important differences are:
- Purpose: Hedging aims to protect while speculation aims to make money
- Risk Profile: Speculators raise risk, while hedgers lower it.
- Time Frame: Speculation is usually short-term, while hedging is usually long-term.
- Market View: Speculators guess which way the market will go, while hedgers get ready for anything.
Examples of Hedging in the Real World
Case Study 1: Southwest Airlines Fuel Hedging
Southwest Airlines famously used fuel hedging to maintain competitive advantage during periods of rising oil prices. By locking in fuel costs through derivatives, they could offer stable pricing while competitors struggled with volatile fuel expenses.
Case Study 2: Apple’s Currency Hedging
Apple hedges a significant portion of its foreign exchange exposure to protect against currency fluctuations. With substantial international sales, currency hedging helps stabilize earnings despite volatile exchange rates.
Case Study 3: Protecting an Individual Investor’s Portfolio
Sarah, who is 55 years old and has a $500,000 portfolio, uses a protective put strategy to protect herself from uncertain market conditions. She buys put options on her biggest investments, which gives her a safety net that limits her losses while still allowing her to make money.
How to Use Hedging Strategies
Step 1: Assess Your Risk Exposure
Find the exact risks in your business or portfolio. Are you exposed to:
- At risk of losing money because of your stock holdings?
- Is there a currency risk with international investments?
- Risk of interest rates from bond positions?
- Is there a risk of commodity prices going up because of business operations?
Step 2: Pick the Right Hedging Tools
Choose hedging tools based on how much risk you can handle, how long you want to hold them, and how much you can afford to spend. Options are good for individual investors, but companies might like forwards or swaps better.
Step 3: Find out what the hedge ratios are.
Choose how much of your exposure to hedge. Full hedging (100%) gives you the most protection, but it also limits your potential for growth. Partial hedging (25–75%) strikes a balance between protection and growth.
Step 4: Keep an eye on things and make changes
Hedging is not a strategy that you can just set and forget. Checking your hedges on a regular basis makes sure they stay useful and cost-effective. Change your positions as the market changes and your risk level changes.
Hedging in global finance
Currency hedging in finance becomes crucial when dealing with international investments or business operations. Hedging strategies are important because exchange rates can change a lot and have a big effect on returns.
- Companies that do business in more than one country
- People who own foreign stocks or bonds
- Businesses that import and export and deal with foreign currency
- Investments in real estate around the world
Why Hedging is Important in Today’s Finance
Hedging is very important in today’s global economy, which is connected. It is important for more than just individual portfolios; it also includes:
Stability in the economy
Hedging is a common practice that helps keep the market stable by lowering extreme volatility and systemic risks.
Business Planning
When companies are protected from major risks, they can make better predictions and strategic choices.
Risk Transfer
Hedging lets people who can’t handle risk pass it on to people who are willing to take it on for a fee.





![How to Start an Ecommerce Business in NZ [2025 Guide]](https://businesskiwi.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/How-to-Start-an-Ecommerce-Business-in-NZ-644-300x200.png)